| .. | ||
| data | ||
| effdet | ||
| img | ||
| scripts | ||
| utils | ||
| waymo_tool | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| bind_launch.py | ||
| distributed_train.sh | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| download_dataset.sh | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| setup.py | ||
| train.py | ||
| validate.py | ||
EfficientDet For PyTorch
This repository provides a script and recipe to train and infer on EfficientDet to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and is tested and maintained by NVIDIA.
Table Of Contents
- Model overview
- Setup
- Quick start guide
- Advanced
- Performance
- Release notes
Model overview
EfficientDet is a convolution-based neural network for the task of object detection. This model is based on EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. NVIDIA's implementation of EfficientDet PyTorch is an optimized version of TensorFlow Model Garden implementation, leveraging mixed precision arithmetic on NVIDIA Volta, NVIDIA Turing, and the NVIDIA Ampere GPU architectures for faster training times while maintaining target accuracy.
The repository also contains scripts to launch training, benchmarking, and inference routines in a Docker container interactively.
The major differences between the official implementation of the paper and our version of EfficientDet are as follows:
- Mixed precision support with PyTorch AMP.
- Multi-node training support.
- Custom fused CUDA kernels for faster computations.
- Lightweight logging using dllogger
- PyTorch multi-tensor ops for faster computation.
These techniques/optimizations improve model performance and reduce training time by a factor of 1.3x, allowing you to perform more efficient object detection with no additional effort.
Other publicly available implementations of EfficientDet include:
Model architecture
EfficientDet is a one-stage detector with the following architecture components:
- ImageNet-pretrained EfficientNet backbone
- Weighted bi-directional feature pyramid network (BiFPN)
- Bounding and classification box head
- A compound scaling method that uniformly scales the resolution, depth, and width for all backbone, feature network, and box/class prediction networks at the same time
Default Configuration
The default configuration of this model can be found at train.py. The default hyper-parameters are as follows:
-
General:
- Base Global Learning Rate set to 0.01
- Epochs set to 300
- Local train batch size - 32
- Local test batch size - 32
-
Backbone:
- Backend network set to EfficientNet-B0
This repository implements multi-gpu to support larger batches and mixed precision support. This implementation also includes the following optimizations.
-
Custom CUDA kernels for Focal Loss and NMS.
-
Custom optimized implementation of EMA.
The source files can be found under
effdet/csrc.
Feature support matrix
The model supports the following features.
| Feature | EfficientDet |
|---|---|
| PyTorch native AMP | Yes |
| PyTorch native DDP | Yes |
| Custom Fused CUDA kernels | Yes |
Features
PyTorch native AMP is part of PyTorch, which provides convenience methods for mixed precision.
DDP stands for DistributedDataParallel and is used for multi-GPU training.
Mixed precision training
Mixed precision is the combined use of different numerical precisions in a computational method. Mixed precision training offers significant computational speedup by performing operations in half-precision format while storing minimal information in single-precision to retain as much information as possible in critical parts of the network. Since the introduction of tensor cores in NVIDIA Volta, and following with both the NVIDIA Turing and NVIDIA Ampere Architectures, significant training speedups are observed by switching to mixed precision—up to 3x overall speedup on the most arithmetically intense model architectures. Using mixed precision training requires two steps:
-
Porting the model to use the FP16 data type where appropriate.
-
Adding loss scaling to preserve small gradient values.
For information about:
-
How to train using mixed precision, refer to the Mixed Precision Training paper and Training With Mixed Precision documentation.
-
Techniques used for mixed precision training, refer to the Mixed-Precision Training of Deep Neural Networks blog.
NVIDIA Apex tools for mixed precision training, refer to the NVIDIA Apex: Tools for Easy Mixed-Precision Training in PyTorch.
Enabling mixed precision
In this repository, mixed precision training is enabled by the PyTorch native AMP library. PyTorch has an automatic mixed precision module that allows mixed precision to be enabled with minimal code changes.
Automatic mixed precision can be enabled with the following code changes:
# Create gradient scaler
scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler(enabled=args.amp)
# Wrap the forward pass and loss in torch.cuda.amp.autocast
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=args.amp):
output = model(input, target)
loss = output['loss']
Where args.amp is the flag to turn on or off AMP. Shell scripts all have a positional argument --amp available to enable mixed precision training.
Enabling TF32
TensorFloat-32 (TF32) is the new math mode in NVIDIA A100 GPUs for handling the matrix math, also called tensor operations. TF32 running on Tensor Cores in A100 GPUs can provide up to 10x speedups compared to single-precision floating-point math (FP32) on NVIDIA Volta GPUs.
TF32 Tensor Cores can speed up networks using FP32, typically with no loss of accuracy. It is more robust than FP16 for models that require a high dynamic range for weights or activations.
For more information, refer to the TensorFloat-32 in the A100 GPU Accelerates AI Training, HPC up to 20x blog post.
TF32 is supported in the NVIDIA Ampere GPU architecture and is enabled by default.
Setup
The following sections list the requirements in order to start training the EfficientDet model.
Requirements
This repository contains Dockerfile which extends the PyTorch NGC container and encapsulates some dependencies. Aside from these dependencies, ensure you have the following components:
- NVIDIA Docker
- PyTorch 21.06-py3 NGC container
- Supported GPUs:
- NVIDIA Volta architecture
- NVIDIA Turing architecture
- NVIDIA Ampere architecture
For more information about how to get started with NGC containers, refer to the following sections from the NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation and the Deep Learning Documentation:
- Getting Started Using NVIDIA GPU Cloud
- Accessing And Pulling From The NGC Container Registry
- Running PyTorch
For those unable to use the Pytorch NGC container, to set up the required environment or create your own container, refer to the versioned NVIDIA Container Support Matrix.
Quick Start Guide
To train your model using mixed or TF32 precision with Tensor Cores or using FP32, perform the following steps using the default parameters of the EfficientDet on the COCO 2017 dataset. For the specifics concerning training and inference, refer to the Advanced section.
1. Clone the repository.
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples.git
cd DeepLearningExamples/PyTorch/Detection/EfficientDet
2. Download and preprocess the dataset.
This repository provides scripts to download and extract the COCO 2017 dataset. Data will be downloaded to the current working directory on the host and extracted to a user-defined directory
To download, verify, and extract the COCO dataset, use the following scripts:
./download_dataset.sh <data/dir>
By default, the data is organized into the following structure:
<data/dir>
annotations/
instances_train2017.json
instances_val2017.json
train2017/
COCO_train2017_*.jpg
val2017/
COCO_val2017_*.jpg
3. Build the EfficientDet PyTorch NGC container.
bash scripts/docker/build.sh
4. Start an interactive session in the NGC container to run training/inference.
After you build the container image, you can start an interactive CLI session with
bash scripts/docker/launch.sh
The launch.sh script requires that the location on the dataset is specified in the script.
5. Start training.
bash ./scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{V100-32G, A100-80G}.sh
The training scripts train an EfficientDet-D0 model and performs evaluation on the COCO 2017 dataset. By default, the training script run training on standard configuration (DGX A100/DGX-1 V100, AMP/FP32/TF32, 300 epochs). Run one of the scripts in ./scripts/D0 directory using bash ./scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{V100-32G, A100-80G}.sh. Ensure COCO-2017 is mounted in /workspace/object_detection/datasets/coco and EfficientNet-B0 backbone weights are mounted in /backbone_checkpoints. The backbone checkpoint can be downloaded from this location.
6. Start validation/evaluation.
To run validation/evaluation for a standard configuration (DGX A100/DGX-1 V100, AMP/TF32/FP32, EfficientDet-D0),
run one of the scripts in the ./scripts/D0 directory using bash ./scripts/D0/validation_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{A100-80G, V100-16G, V100-32G}.sh.
Ensure COCO-2017 is mounted in /workspace/object_detection/datasets/coco.
(Optional) Mount the checkpoint in the /checkpoints location to evaluate on a checkpoint and in the script add the path to the checkpoint as --checkpoint /checkpoints/<NAME OF CHECKPOINT>.
7. Start inference/predictions.
Model predictions can be obtained on a test dataset and a model checkpoint by running the scripts/D0/inference_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_{A100-80G, V100-32G}.sh script. The script requires:
- the location of the checkpoint folder and dataset to be specified and present within/mounted to the container.
- number of GPUs to run inference on.
For example:
NUM_PROC=<number_of_processes> CKPT_PATH=<checkpoint_path> BATCH_SIZE=<batch_size> bash scripts/inference_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_{A100-80G, V100-32G}.sh
Model prediction files get saved in the --results path if provided; otherwise, they will be saved in the current working directory.
To perform just inference and skip computation of mAP scores, use the --inference flag.
Advanced
The following sections provide greater details of the dataset, running training and inference, and the training results.
Scripts and sample code
Descriptions of the key scripts and folders are provided below.
-
effdet - Contains code to build individual components of the model such as backbone, FPN, RPN, classification and bbox heads, and so on.
-
data - Contains code to build the data pipeline such as dataloader, transforms, dataset builder.
-
download_dataset.sh - Launches download and processing of required datasets.
dtrxpackage needs to be installed for this script to run without errors. -
scripts/ - Contains shell scripts to launch training and evaluation of the model and perform inferences.
-
D0/train_{AMP, TF32, FP32}_8x{V100-32G, A100-80G}.sh - Launches model training
-
D0/evaluation_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{A100-80G, V100-16G, V100-32G}.sh - Performs inference and computes mAP of predictions.
-
docker/ - Scripts to build the docker image and to start an interactive session.
-
-
utils/
- Contains utility components like samplers, EMA, optimizers, schedulers, and so on.
-
train.py - End to end to script to load data, build and train the model.
-
validate.py - End to end script to load data, checkpoint and perform inference and compute mAP score.
Parameters
train.py script parameters
Important parameters for training are listed below with defaults.
Command-line options
To display the full list of available options and their descriptions, use the -h or --help command-line option, for example:
data- Path to coco datasetmodel- Name of the model to train (default: "efficientdet_d0")lr- Learning rateepochs- Maximum number of epochs to train forwarmup-epochs- Epochs to warmup LR, if scheduler supportsbatch-size- Input batch size
python train.py --help will give all the command-line parameters specific to train.py:
--model MODEL Name of the model to train (default: "countception"
--redundant-bias Override model config for redundant bias
--no-redundant-bias Override model config for redundant bias
--pretrained Start with the pretrained version of a specified network (if avail)
--pretrained-backbone-path PATH
Start from pre-trained backbone weights.
--initial-checkpoint PATH
Initialize model from this checkpoint (default: none)
--resume Resume full model and optimizer state from checkpoint (default: False)
--no-resume-opt Prevent resume of optimizer state when resuming model
--interpolation NAME Image resize interpolation type (overrides model)
--fill-color NAME Image augmentation fill (background) color ("mean" or int)
-b N, --batch-size N input batch size for training (default: 32)
-vb N, --validation-batch-size-multiplier N
ratio of validation batch size to training batch size (default: 1)
--input_size PCT Image size (default: None) if this is not set default model image size is taken
--drop PCT Dropout rate (default: 0.)
--clip-grad NORM Clip gradient norm (default: 10.0)
--opt OPTIMIZER Optimizer (default: "momentum"
--opt-eps EPSILON Optimizer Epsilon (default: 1e-3)
--momentum M SGD momentum (default: 0.9)
--weight-decay WEIGHT_DECAY
weight decay (default: 0.00004)
--sched SCHEDULER LR scheduler (default: "step"
--lr LR learning rate (default: 0.01)
--lr-noise pct, pct [pct, pct ...]
learning rate noise on/off epoch percentages
--lr-noise-pct PERCENT
learning rate noise limit percent (default: 0.67)
--lr-noise-std STDDEV
learning rate noise std-dev (default: 1.0)
--lr-cycle-mul MULT learning rate cycle len multiplier (default: 1.0)
--lr-cycle-limit N learning rate cycle limit
--warmup-lr LR warmup learning rate (default: 0.0001)
--min-lr LR lower lr bound for cyclic schedulers that hit 0 (1e-5)
--epochs N number of epochs to train (default: 2)
--start-epoch N manual epoch number (useful on restarts)
--decay-epochs N epoch interval to decay LR
--warmup-epochs N epochs to warmup LR, if scheduler supports
--cooldown-epochs N epochs to cooldown LR at min_lr, after cyclic schedule ends
--patience-epochs N patience epochs for Plateau LR scheduler (default: 10
--decay-rate RATE, --dr RATE
LR decay rate (default: 0.1)
--mixup MIXUP mixup alpha, mixup enabled if > 0. (default: 0.)
--mixup-off-epoch N turn off mixup after this epoch, disabled if 0 (default: 0)
--smoothing SMOOTHING
label smoothing (default: 0.0)
--train-interpolation TRAIN_INTERPOLATION
Training interpolation (random, bilinear, bicubic default: "random")
--sync-bn Enable NVIDIA Apex or Torch synchronized BatchNorm.
--dist-bn DIST_BN Distribute BatchNorm stats between nodes after each epoch ("broadcast", "reduce", or "")
--model-ema Enable tracking moving average of model weights
--model-ema-decay MODEL_EMA_DECAY
decay factor for model weights moving average (default: 0.9998)
--dist-group-size DIST_GROUP_SIZE
Group size for sync-bn
--seed S random seed (default: 42)
--log-interval N how many batches to wait before logging training status
--eval-after N Start evaluating after eval-after epochs
--benchmark Turn this on when measuring performance
--benchmark-steps N Run training for this number of steps for performance measurement
--dllogger-file PATH File name of dllogger json file (default: log.json, current dir)
--save-checkpoint-interval N
Save checkpoints after so many epochs
-j N, --workers N how many training processes to use (default: 1)
--amp use NVIDIA amp for mixed precision training
--no-pin-mem Disable pin CPU memory in DataLoader.
--no-prefetcher disable fast prefetcher
--output PATH path to the output folder (default: none, current dir)
--eval-metric EVAL_METRIC
Best metric (default: "map"
--local_rank LOCAL_RANK
--memory-format {nchw,nhwc}
memory layout, nchw or nhwc
--fused-focal-loss Use fused focal loss for better performance.
--waymo Train on Waymo dataset or COCO dataset. Default: False (COCO dataset)
--num_classes PCT Number of classes the model needs to be trained for (default: None)
--remove-weights [REMOVE_WEIGHTS [REMOVE_WEIGHTS ...]]
Remove these weights from the state dict before loading checkpoint (use case can be not loading heads)
--freeze-layers [FREEZE_LAYERS [FREEZE_LAYERS ...]]
Freeze these layers
--waymo-train-annotation WAYMO_TRAIN_ANNOTATION
Absolute Path to waymo training annotation (default: "None")
--waymo-val-annotation WAYMO_VAL_ANNOTATION
Absolute Path to waymo validation annotation (default: "None")
--waymo-train WAYMO_TRAIN
Path to waymo training relative to waymo data (default: "None")
--waymo-val WAYMO_VAL
Path to waymo validation relative to waymo data (default: "None")
Getting the data
By default, the EfficientDet model is trained on the COCO 2017 dataset. This dataset comes with a training and validation set.
This repository contains the ./download_dataset.sh scripts that automatically downloads and preprocesses the training and validation sets.
Dataset guidelines
This repository contains the ./download_dataset.sh scripts that automatically downloads and preprocesses the training and validation sets.
This repository also provides support for fine-tuning and evaluating on Waymo dataset. In order to run on the Waymo dataset, ensure your dataset is present/mounted to the Docker container and the dataset is in COCO format. For that, this repository has scripts to download, preprocess and convert Waymo dataset into COCO format, which is ingestible by EfficientDet.
waymo_tool/waymo_data_converter.py- downloads and converts the data into COCO format
Since the original Waymo dataset is in TFRecords format, to convert it into COCO format, Tensorflow needs to be installed.
Training Process
Training is performed using the train.py script. The default parameters can be overridden by command-line arguments.
The training process can start from scratch or resume from a checkpoint.
By default, bash script scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{A100-80G, V100-32G}.sh will start the training process from scratch with the following settings.
- Use 8 GPUs
- Saves checkpoints after every 10 epochs to
/workspace/output/folder - AMP or FP32 or TF32 based on the folder
scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_8x{A100-80G, V100-32G}.sh
To resume from a checkpoint, include --resume in the command-line and place the checkpoint into /workspace/output/.
Multi-node
Multi-node runs can be launched on a Pyxis/enroot Slurm cluster (see Requirements) with the ./scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32}_32xV100-32G.sub script with the following command for a 4-node NVIDIA DGX V100 example:
sbatch N 4 --ntasks-per-node=8 ./scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32}_32xV100-32G.sub
Note that the ./scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32}_32xV100-32G.sub script is a starting point that has to be adapted depending on the environment. In particular, variables such as --container-image handle the container image to train using, and datadir handle the location of the COCO-2017 data. The backbone (EfficientNet) weights need to be put in /backbone_checkpoints.
Refer to the files contents to view the full list of variables to adjust for your system.
Performance
Benchmarking
Benchmarking can be performed for both training and inference. Both the scripts run the EfficientDet model. You can specify whether benchmarking is performed in AMP, TF32, or FP32 by specifying it as an argument to the benchmarking scripts.
Training performance benchmark
Training benchmarking can be performed by running the script:
scripts/D0/train-benchmark_{AMP, TF32, FP32}_{V100-32G, A100-80G}.sh
Inference performance benchmark
Inference benchmarking can be performed by running the script:
scripts/D0/inference_{AMP, FP32, TF32}_{A100-80G, V100-32G}.sh
Results
The following sections provide details on how we achieved our performance and accuracy in training and inference.
Training Accuracy Results
Training accuracy: NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/D0/train_{AMP, TF32}_8xA100-80G.sh training script in the 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB) GPUs with no intermediate evaluation.
| GPUs | BBOX mAP - TF32 | BBOX mAP - FP16 | Time to train - TF32 | Time to train - mixed precision | Time to train - speedup (TF32 to mixed precision) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.3399 | 0.3407 | 8.57 | 6.5 | 1.318 |
Training accuracy: NVIDIA DGX-1 (8x V100 32GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32}_8xV100-32G.sh training script in the PyTorch 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with 8x V100 32GB GPUs with no intermediate evaluation.
| GPUs | BBOX mAP - FP32 | BBOX mAP - FP16 | Time to train - FP32 | Time to train - mixed precision | Time to train - speedup (FP32 to mixed precision) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.3410 | 0.3413 | 16 | 10.5 | 1.52 |
Training accuracy: NVIDIA DGX-1 (32x V100 32GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/D0/train_{AMP, FP32}_32xV100-32G.sh training script in the PyTorch 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with 32x V100 32GB GPUs with no intermediate evaluation.
| GPUs | BBOX mAP - FP32 | BBOX mAP - FP16 | Time to train - FP32 | Time to train - mixed precision | Time to train - speedup (FP32 to mixed precision) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 32 | 0.3418 | 0.3373 | 6 | 4.95 | 1.22 |
Training accuracy on Waymo dataset: NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/waymo/train_waymo_AMP_8xA100-80G.sh training script in the 21.06-py3 NGC container on the Waymo dataset on NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB) GPUs with no intermediate evaluation. These results were obtained by training the EfficientDet-D0 model with a frozen backbone.
| category | mAP | category | AP @ IoU 0.7 | category | AP @ IoU 0.5 | category | AP @ IoU 0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2_ALL_NS | 50.377 | Vehicle | 50.271 | Pedestrian | 61.788 | Cyclist | 39.072 |
The following results were obtained by training the EfficientDet-D0 model without freezing any part of the architecture. This can be done by removing the --freeze_layer argument from the script.
| category | mAP | category | AP @ IoU 0.7 | category | AP @ IoU 0.5 | category | AP @ IoU 0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L2_ALL_NS | 51.249 | Vehicle | 51.091 | Pedestrian | 62.816 | Cyclist | 39.841 |
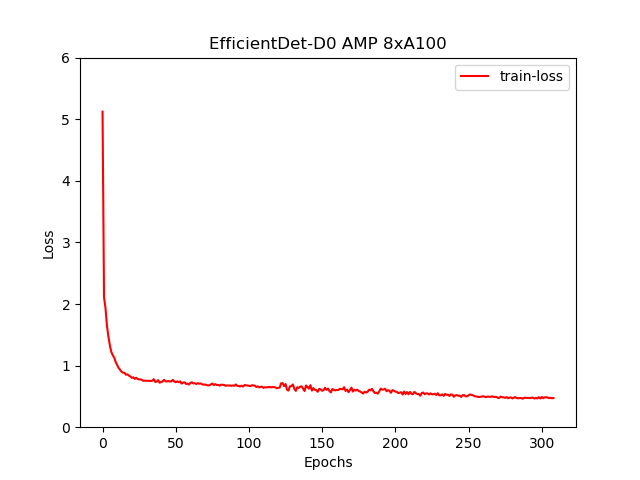
Training loss curves
Here, multihead loss is simply the weighted sum of losses on the classification head and the bounding box head.
Training Stability Test
The following tables compare mAP scores across five different training runs with different seeds. The runs showcase consistent convergence on all five seeds with very little deviation.
| Config | Seed 1 | Seed 2 | Seed 3 | Seed 4 | Seed 5 | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 GPUs, final AP BBox | 0.3422 | 0.3379 | 0.3437 | 0.3424 | 0.3402 | 0.3412 | 0.002 |
Training Performance Results
Training performance: NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/D0/train_benchmark_{AMP, TP32}_8xA100-80G.sh training script in the 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB) GPUs. Performance numbers in images per second were averaged over an entire training epoch.
| GPUs | Throughput - TF32 | Throughput - mixed precision | Throughput speedup (TF32 - mixed precision) | Weak scaling - TF32 | Weak scaling - mixed precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 170 | 255 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 616 | 866 | 1.4 | 3.62 | 3.39 |
| 8 | 1213 | 1835 | 1.5 | 7.05 | 7.05 |
Training performance: NVIDIA DGX-1 (8x V100 32GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/D0/train_benchmark_{AMP, FP32}_8xV100-32G.sh training script in the 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with (8x V100 32GB) GPUs. Performance numbers in images per second were averaged over an entire training epoch.
| GPUs | Throughput - FP32 | Throughput - mixed precision | Throughput speedup (FP32 - mixed precision) | Weak scaling - FP32 | Weak scaling - mixed precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 110 | 186 | 1.69 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 367 | 610 | 1.66 | 3.33 | 3.28 |
| 8 | 613 | 1040 | 1.69 | 5.57 | 5.59 |
To achieve similar results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Inference performance results
Inference performance: NVIDIA DGX A100 (1x A100 40GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/inference_{AMP, TF32}_A100-80G.sh training script in the PyTorch 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (1x A100 80GB) GPU.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Throughput - TF32 | Throughput - mixed precision | Throughput speedup (TF32 - mixed precision) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 45.61 | 50.23 | 1.101 |
To achieve similar results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Inference performance: NVIDIA DGX-1 (1x V100 32GB)
Our results were obtained by running the scripts/inference_{AMP, FP32}_V100-32G.sh training script in the PyTorch 21.06-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with 1x V100 32GB GPUs. Performance numbers (in items/images per second) were averaged over an entire training epoch.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Throughput - FP32 | Throughput - mixed precision | Throughput speedup (FP32 - mixed precision) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 38.81 | 42.25 | 1.08 |
To achieve these same results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Release notes
Changelog
July 2021
- Initial Release
Known Issues
There are no known issues with this model.