| cmd | ||
| docs | ||
| examples | ||
| lib | ||
| pkg | ||
| tools/mujs | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| glide.lock | ||
| glide.yaml | ||
| main.go | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
Mu
Mu is a framework and toolset for creating reusable stacks of services.
If you are learning about Mu for the first time, please see the overview document.
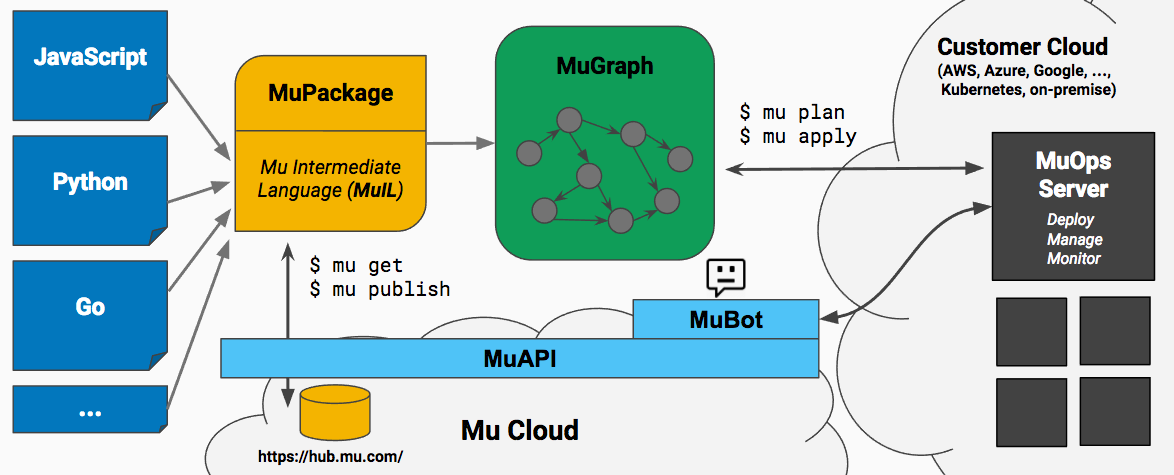
Architecture
Building and Testing
To build Mu, first clone it into a standard Go workspace:
$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/marapongo
$ git clone git@github.com:marapongo/mu $GOPATH/src/github.com/marapongo/mu
A good default value for GOPATH is ~/go.
Mu needs to know where to look for its runtime, library, etc. By default, it will look in /usr/local/mu, however you
can override this with the MUPATH variable. Normally it's easiest just to create a symlink:
$ ln -s $GOPATH/src/github.com/marapongo/mu /usr/local/mu
There is one additional build-time dependency, golint, which can be installed using:
$ go get -u github.com/golang/lint/golint
And placed on your path by:
$ export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
At this point you should be able to build and run tests from the root directory:
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/marapongo/mu
$ make
This installs the mu binary into $GOPATH/bin, which may now be run provided make exited successfully.
Debugging
The Mu tools have extensive logging built in. In fact, we encourage liberal logging in new code, and addding new logging when debugging problems. This helps to ensure future debugging endeavors benefit from your sleuthing.
All logging is done using Google's Glog library. It is relatively barebones, and adds basic leveled logging, stack dumping, and other capabilities beyond what Go's built-in logging routines offer.
The Mu command line has two flags that control this logging and that can come in handy when debugging problems. The
--logtostderr flag spews directly to stderr, rather than the default of logging to files in your temp directory. And
the --verbose=n flag (-v=n for short) sets the logging level to n. Anything greater than 3 is reserved for
debug-level logging, greater than 5 is going to be quite verbose, and anything beyond 7 is extremely noisy.
For example, the command
$ mu compile blueprint.yaml --logtostderr -v=5
is a pretty standard starting point during debugging that will show a fairly comprehensive trace log of a compilation.