13 KiB
Deploying the SE-ResNeXt101-32x4d model using Triton Inference Server
The NVIDIA Triton Inference Server provides a datacenter and cloud inferencing solution optimized for NVIDIA GPUs. The server provides an inference service via an HTTP or gRPC endpoint, allowing remote clients to request inferencing for any number of GPU or CPU models being managed by the server.
This folder contains instructions on how to deploy and run inference on Triton Inference Server as well as gather detailed performance analysis.
Table Of Contents
Model overview
The SE-ResNeXt101-32x4d is a ResNeXt101-32x4d model with added Squeeze-and-Excitation module introduced in Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks paper.
The SE-ResNeXt101-32x4d model can be deployed for inference on the NVIDIA Triton Inference Server using TorchScript, ONNX Runtime or TensorRT as an execution backend.
Setup
This script requires trained SE-ResNeXt101-32x4d model checkpoint that can be used for deployment.
Inference container
For easy-to-use deployment, a build script for special inference container was prepared. To build that container, go to the main repository folder and run:
docker build -t sernxt_inference . -f triton/Dockerfile
This command will download the dependencies and build the inference containers. Then, run shell inside the container:
docker run -it --rm --gpus device=0 --shm-size=1g --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 --net=host -v <PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY>:/repository sernxt_inference bash
Here device=0,1,2,3 selects the GPUs indexed by ordinals 0,1,2 and 3, respectively. The server will see only these GPUs. If you write device=all, then the server will see all the available GPUs. PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY indicates location to where the
deployed models were stored.
Deploying the model
To deploy the SE-ResNext101-32x4d model into the Triton Inference Server, you must run the deployer.py script from inside the deployment Docker container to achieve a compatible format.
usage: deployer.py [-h] (--ts-script | --ts-trace | --onnx | --trt)
[--triton-no-cuda] [--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME]
[--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION]
[--triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL]
[--triton-max-batch-size TRITON_MAX_BATCH_SIZE]
[--triton-dyn-batching-delay TRITON_DYN_BATCHING_DELAY]
[--triton-engine-count TRITON_ENGINE_COUNT]
[--save-dir SAVE_DIR]
[--max_workspace_size MAX_WORKSPACE_SIZE] [--trt-fp16]
[--capture-cuda-graph CAPTURE_CUDA_GRAPH]
...
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--ts-script convert to torchscript using torch.jit.script
--ts-trace convert to torchscript using torch.jit.trace
--onnx convert to onnx using torch.onnx.export
--trt convert to trt using tensorrt
triton related flags:
--triton-no-cuda Use the CPU for tracing.
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME
exports to appropriate directory structure for TRITON
--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION
exports to appropriate directory structure for TRITON
--triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL
exports to appropriate directory structure for TRITON
--triton-max-batch-size TRITON_MAX_BATCH_SIZE
Specifies the 'max_batch_size' in the TRITON model
config. See the TRITON documentation for more info.
--triton-dyn-batching-delay TRITON_DYN_BATCHING_DELAY
Determines the dynamic_batching queue delay in
milliseconds(ms) for the TRITON model config. Use '0'
or '-1' to specify static batching. See the TRITON
documentation for more info.
--triton-engine-count TRITON_ENGINE_COUNT
Specifies the 'instance_group' count value in the
TRITON model config. See the TRITON documentation for
more info.
--save-dir SAVE_DIR Saved model directory
optimization flags:
--max_workspace_size MAX_WORKSPACE_SIZE
set the size of the workspace for trt export
--trt-fp16 trt flag ---- export model in mixed precision mode
--capture-cuda-graph CAPTURE_CUDA_GRAPH
capture cuda graph for obtaining speedup. possible
values: 0, 1. default: 1.
model_arguments arguments that will be ignored by deployer lib and
will be forwarded to your deployer script
Following model specific arguments have to be specified for model deployment:
--config CONFIG Network architecture to use for deployment (eg. resnet50,
resnext101-32x4d or se-resnext101-32x4d)
--checkpoint CHECKPOINT
Path to stored model weight. If not specified, model will be
randomly initialized
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Batch size used for dummy dataloader
--fp16 Use model with half-precision calculations
For example, to deploy model into TensorRT format, using half precision and max batch size 64 called
sernxt-trt-16 execute:
python -m triton.deployer --trt --trt-fp16 --triton-model-name sernxt-trt-16 --triton-max-batch-size 64 --save-dir /repository -- --config se-resnext101-32x4d --checkpoint model_checkpoint --batch_size 64 --fp16
Where model_checkpoint is a checkpoint for a trained model with the same architecture (se-resnext101-32x4d) as used during export.
Running the Triton Inference Server
NOTE: This step is executed outside the inference container.
Pull the Triton Inference Server container from our repository:
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:20.07-py3
Run the command to start the Triton Inference Server:
docker run -d --rm --gpus device=0 --ipc=host --network=host -p 8000:8000 -p 8001:8001 -p 8002:8002 -v <PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY>:/models nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:20.07-py3 trtserver --model-store=/models --log-verbose=1 --model-control-mode=poll --repository-poll-secs=5
Here device=0,1,2,3 selects GPUs indexed by ordinals 0,1,2 and 3, respectively. The server will see only these GPUs. If you write device=all, then the server will see all the available GPUs. PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY indicates the location where the
deployed models were stored. An additional --model-controle-mode option allows to reload the model when it changes in the filesystem. It is a required option for benchmark scripts that works with multiple model versions on a single Triton Inference Server instance.
Quick Start Guide
Running the client
The client client.py checks the model accuracy against synthetic or real validation
data. The client connects to Triton Inference Server and performs inference.
usage: client.py [-h] --triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME [-v]
[--inference_data INFERENCE_DATA] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE]
[--fp16]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL
URL adress of trtion server (with port)
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME
Triton deployed model name
-v, --verbose Verbose mode.
--inference_data INFERENCE_DATA
Path to file with inference data.
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Inference request batch size
--fp16 Use fp16 precision for input data
To run inference on the model exported in the previous steps, using the data located under
/dataset, run:
python -m triton.client --triton-server-url localhost:8001 --triton-model-name sernxt-trt-16 --inference_data /data/test_data.bin --batch_size 16 --fp16
Gathering performance data
Performance data can be gathered using the perf_client tool. To use this tool to measure performance for batch_size=32, the following command can be used:
/workspace/bin/perf_client --max-threads 10 -m sernxt-trt-16 -x 1 -p 10000 -v -i gRPC -u localhost:8001 -b 32 -l 5000 --concurrency-range 1 -f result.csv
For more information about perf_client, refer to the documentation.
Advanced
Automated benchmark script
To automate benchmarks of different model configurations, a special benchmark script is located in triton/scripts/benchmark.sh. To use this script,
run Triton Inference Server and then execute the script as follows:
bash triton/scripts/benchmark.sh <MODEL_REPOSITORY> <LOG_DIRECTORY> <ARCHITECTURE> (<CHECKPOINT_PATH>)
The benchmark script tests all supported backends with different batch sizes and server configuration. Logs from execution will be stored in <LOG DIRECTORY>.
To process static configuration logs, triton/scripts/process_output.sh script can be used.
Performance
The performance measurements in this document were conducted at the time of publication and may not reflect the performance achieved from NVIDIA’s latest software release. For the most up-to-date performance measurements, go to NVIDIA Data Center Deep Learning Product Performance.
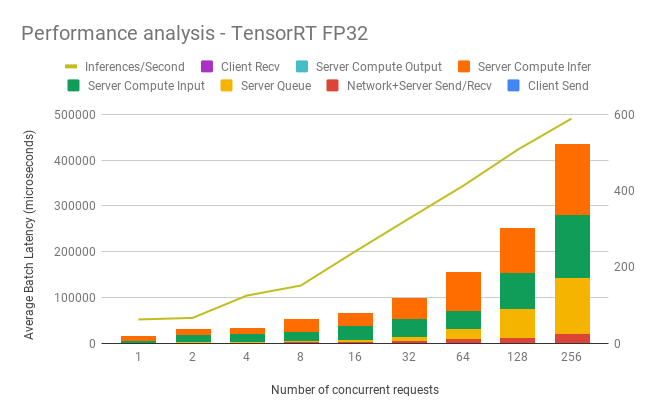
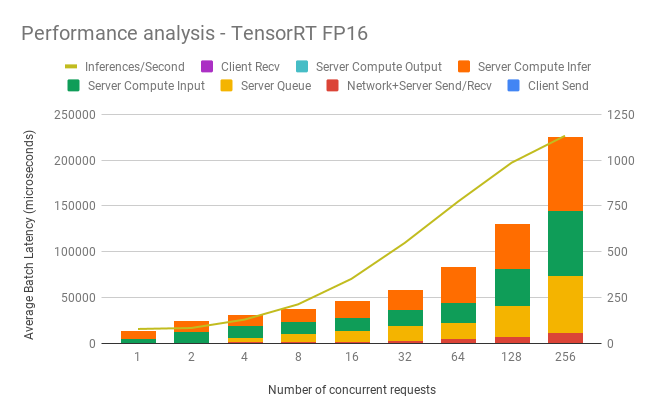
Dynamic batching performance
The Triton Inference Server has a dynamic batching mechanism built-in that can be enabled. When it is enabled, the server creates inference batches from multiple received requests. This allows us to achieve better performance than doing inference on each single request. The single request is assumed to be a single image that needs to be inferenced. With dynamic batching enabled, the server will concatenate single image requests into an inference batch. The upper bound of the size of the inference batch is set to 64. All these parameters are configurable.
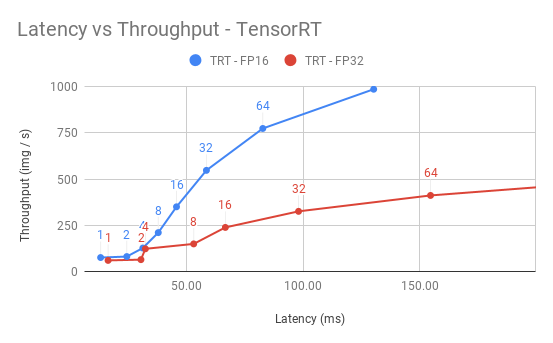
Our results were obtained by running automated benchmark script. Throughput is measured in images/second, and latency in milliseconds.
TensorRT backend inference performance (1x V100 16GB)
FP32 Inference Performance
| Concurrent requests | Throughput (img/s) | Avg. Latency (ms) | 90% Latency (ms) | 95% Latency (ms) | 99% Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 62.1 | 16.10 | 16.20 | 16.23 | 16.33 |
| 2 | 66.2 | 30.23 | 30.26 | 30.27 | 30.32 |
| 4 | 124.6 | 32.13 | 32.19 | 32.21 | 32.28 |
| 8 | 151.1 | 52.91 | 53.10 | 53.15 | 53.21 |
| 16 | 240 | 66.51 | 66.82 | 66.91 | 67.05 |
| 32 | 326.8 | 98.00 | 132.41 | 134.00 | 137.71 |
| 64 | 412.6 | 154.74 | 182.47 | 185.90 | 195.43 |
| 128 | 506.7 | 252.58 | 275.03 | 277.56 | 279.86 |
| 256 | 588.8 | 434.40 | 435.82 | 436.59 | 444.09 |
FP16 Inference Performance
| Concurrent requests | Throughput (img/s) | Avg. Latency (ms) | 90% Latency (ms) | 95% Latency (ms) | 99% Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 77.5 | 12.90 | 12.98 | 13.01 | 13.05 |
| 2 | 82.8 | 24.15 | 24.23 | 24.25 | 24.30 |
| 4 | 128.8 | 31.06 | 38.81 | 39.15 | 39.31 |
| 8 | 212 | 37.68 | 42.28 | 43.06 | 43.17 |
| 16 | 351.3 | 45.52 | 48.41 | 48.52 | 48.92 |
| 32 | 548 | 58.38 | 59.09 | 59.38 | 59.80 |
| 64 | 774 | 82.63 | 84.40 | 84.88 | 86.49 |
| 128 | 985.7 | 130.30 | 130.83 | 131.26 | 132.86 |
| 256 | 1132.8 | 225.56 | 226.34 | 227.31 | 229.30 |
Release notes
Changelog
September 2020
- Initial release