17 KiB
Deploying the DLRM model using Triton Inference Server
This folder contains instructions for deploment and exemplary client application to run inference on Triton Inference Server as well as detailed performance analysis.
Table Of Contents
Solution Overview
The NVIDIA Triton Inference Server provides a datacenter and cloud inferencing solution optimized for NVIDIA GPUs. The server provides an inference service via an HTTP or gRPC endpoint, allowing remote clients to request inferencing for any number of GPU or CPU models being managed by the server.
Quick Start Guide
Running Triton Inference Server and client
The very first step of deployment is to acquire trained checkpoint and model configuration for this
checkpoint. Default model configuration are stored inside dlrm/config directory.
Currently, our implementation only supports TorchScript deployment for models that fit into the memory of a single GPU. You can read more about training DLRM models on different dataset configurations based on frequency threshold in the preprocessing step in README.
Inference container
Every command below is called from special inference container. To build that container go to main repository folder and call
docker build -t dlrm-inference . -f triton/Dockerfile
This command will download dependencies and build inference container. Then run shell inside the container:
docker run -it --rm --gpus device=0 --shm-size=1g --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 --net=host -v <PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY>:/repository -v <PATH_TO_MODEL_CHECKPOINT>:/results/checkpoint -v <PATH_TO_DATASET>:/data dlrm-inference bash
Here --gpus '"device=0,1,2,3"' selects GPUs indexed by ordinals 0,1,2 and 3, respectively. The server will see only these GPUs. If you write device=all, then the server will see all the available GPUs. PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY indicates location where
deployed models were stored.
Deploying the model
To deploy model into Triton compatible format, deployer.py script can by used. This script is
meant to be run from inside deployment docker container.
usage: deployer.py [-h] (--ts-script | --ts-trace | --onnx) [--triton-no-cuda]
[--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME]
[--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION]
[--triton-max-batch-size TRITON_MAX_BATCH_SIZE]
[--triton-dyn-batching-delay TRITON_DYN_BATCHING_DELAY]
[--triton-engine-count TRITON_ENGINE_COUNT]
[--save-dir SAVE_DIR] [--deploy_cpu]
...
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--ts-script convert to torchscript using torch.jit.script
--ts-trace convert to torchscript using torch.jit.trace
--onnx convert to onnx using torch.onnx.export
--deploy_cpu
triton related flags:
--triton-no-cuda Use the CPU for tracing.
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME
exports to appropriate directory structure for triton
--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION
exports to appropriate directory structure for triton
--triton-max-batch-size TRITON_MAX_BATCH_SIZE
Specifies the 'max_batch_size' in the triton model
config. See the triton documentation for more info.
--triton-dyn-batching-delay TRITON_DYN_BATCHING_DELAY
Determines the dynamic_batching queue delay in
milliseconds(ms) for the triton model config. Use '0'
or '-1' to specify static batching. See the triton
documentation for more info.
--triton-engine-count TRITON_ENGINE_COUNT
Specifies the 'instance_group' count value in the
triton model config. See the triton documentation for
more info.
--save-dir SAVE_DIR Saved model directory
other flags:
model_arguments arguments that will be ignored by deployer lib and
will be forwarded to your deployer script
Following model specific arguments have to be specified for model deployment:
--embedding_dim EMBEDDING_DIM
Embedding dimensionality.
--top_mlp_sizes TOP_MLP_SIZES [TOP_MLP_SIZES ...]
Units in layers of top MLP (default: 1024 1024 512 256 1).
--bottom_mlp_sizes BOTTOM_MLP_SIZES [BOTTOM_MLP_SIZES ...]
Units in layers of bottom MLP (default: 512 256 128).
--interaction_op {cat,dot}
Interaction operator to use.
--dataset DATASET
Path to dataset directory contaning model_size.json file
describing input sizes for each embedding layer.
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Internal dataloader batch size, usually it is the same as batch size
specified in --triton-max-batch_size flag.
--fp16
Set a model for fp16 deployment.
--dump_perf_data DIRECTORY_NAME
Dump binary performance data that can by loaded by perf client.
--model_checkpoint MODEL_CHECKPOINT
Checkpoint file with trained model that is going to be deployed.
--cpu Export cpu model instead of gpu.
For example, to deploy model into TorchScript format, using half precision and max batch size 4096 called
dlrm-ts-trace-16 execute:
python -m triton.deployer --ts-trace --triton-model-name dlrm-ts-trace-16 --triton-max-batch-size 4096 --save-dir /repository -- --model_checkpoint /results/checkpoint --fp16 --batch_size 4096 --num_numerical_features 13 --embedding_dim 128 --top_mlp_sizes 1024 1024 512 256 1 --bottom_mlp_sizes 512 256 128 --interaction_op dot --dataset /data
Where model_checkpoint is a checkpoint for a trained model with the same configuration as used during export and dataset (or at least dataset configuration)
is mounted under /data
Running the Triton server
NOTE: This step is executed outside inference container
docker pull nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:20.09-py3docker run -d --rm --gpus device=0 --ipc=host --network=host [--cpuset-cpus=0-15] -p 8000:8000 -p 8001:8001 -p 8002:8002 -v <PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY>:/models nvcr.io/nvidia/tritonserver:20.09-py3 tritonserver --model-repository=/models --log-verbose=1 --model-control-mode=explicit
Here --gpus '"device=0,1,2,3"' selects GPUs indexed by ordinals 0,1,2 and 3, respectively. The server will see only these GPUs. If you write device=all, then the server will see all the available GPUs. PATH_TO_MODEL_REPOSITORY indicates location where
deployed models were stored. Additional --model-control-mode option allows to manually load and
unload models. This is especially useful when dealing with numerous large models like DLRM.
For models exported to onnx format and hosted inside onnx runtime it might be required to limit visible cpu to fully utlize gpu acceleration. Use --cpuset-cpus docker option for that.
Running client
Exemplary client client.py allows to check model performance against synthetic or real validation
data. Client connects to Triton server and perform inference.
usage: client.py [-h] --triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME
[--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION] [-v]
[-H HTTP_HEADER] --dataset_config DATASET_CONFIG
[--inference_data INFERENCE_DATA] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE]
[--drop_last_batch DROP_LAST_BATCH] [--fp16]
[--test_batches TEST_BATCHES]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--triton-server-url TRITON_SERVER_URL
URL adress of triton server (with port)
--triton-model-name TRITON_MODEL_NAME
Triton deployed model name
--triton-model-version TRITON_MODEL_VERSION
Triton model version
-v, --verbose Enable verbose output
-H HTTP_HEADER HTTP headers to add to inference server requests.
Format is -H"Header:Value".
--dataset_config DATASET_CONFIG
--inference_data INFERENCE_DATA
Path to file with inference data.
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Inference request batch size
--drop_last_batch DROP_LAST_BATCH
Drops the last batch size if it's not full
--fp16 Use 16bit for numerical input
--test_batches TEST_BATCHES
Specifies number of batches used in the inference
To run inference on model exported in previous steps, using data located under
/data/test execute:
python -m triton.client --triton-server-url localhost:8000 --triton-model-name dlrm-ts-trace-16 --dataset_config /data/model_size.json --inference_data /data/test --batch_size 4096 --fp16
Gathering performance data
Performance data can be gathered using perf_client tool. To use this tool, performance data needs
to be dumped during deployment. To do that, use --dump_perf_data option for the deployer:
python -m triton.deployer --ts-trace --triton-model-name dlrm-ts-trace-16 --triton-max-batch-size 4096 --save-dir /repository -- --model_checkpoint /results/checkpoint --fp16 --batch_size 4096 --num_numerical_features 13 --embedding_dim 128 --top_mlp_sizes 1024 1024 512 256 1 --bottom_mlp_sizes 512 256 128 --interaction_op dot --dataset /data --dump_perf_data /location/for/perfdata
When perf data are dumped, perf_client can be used with following command:
/workspace/bin/perf_client --max-threads 10 -m dlrm-ts-trace-16 -x 1 -p 5000 -v -i gRPC -u localhost:8001 -b 4096 -l 5000 --concurrency-range 1 --input-data /location/for/perfdata -f result.csv
For more information about perf_client please refer to official documentation.
Performance
The performance measurements in this document were conducted at the time of publication and may not reflect the performance achieved from NVIDIA’s latest software release. For the most up-to-date performance measurements, go to NVIDIA Data Center Deep Learning Product Performance.
Throughput/Latency results
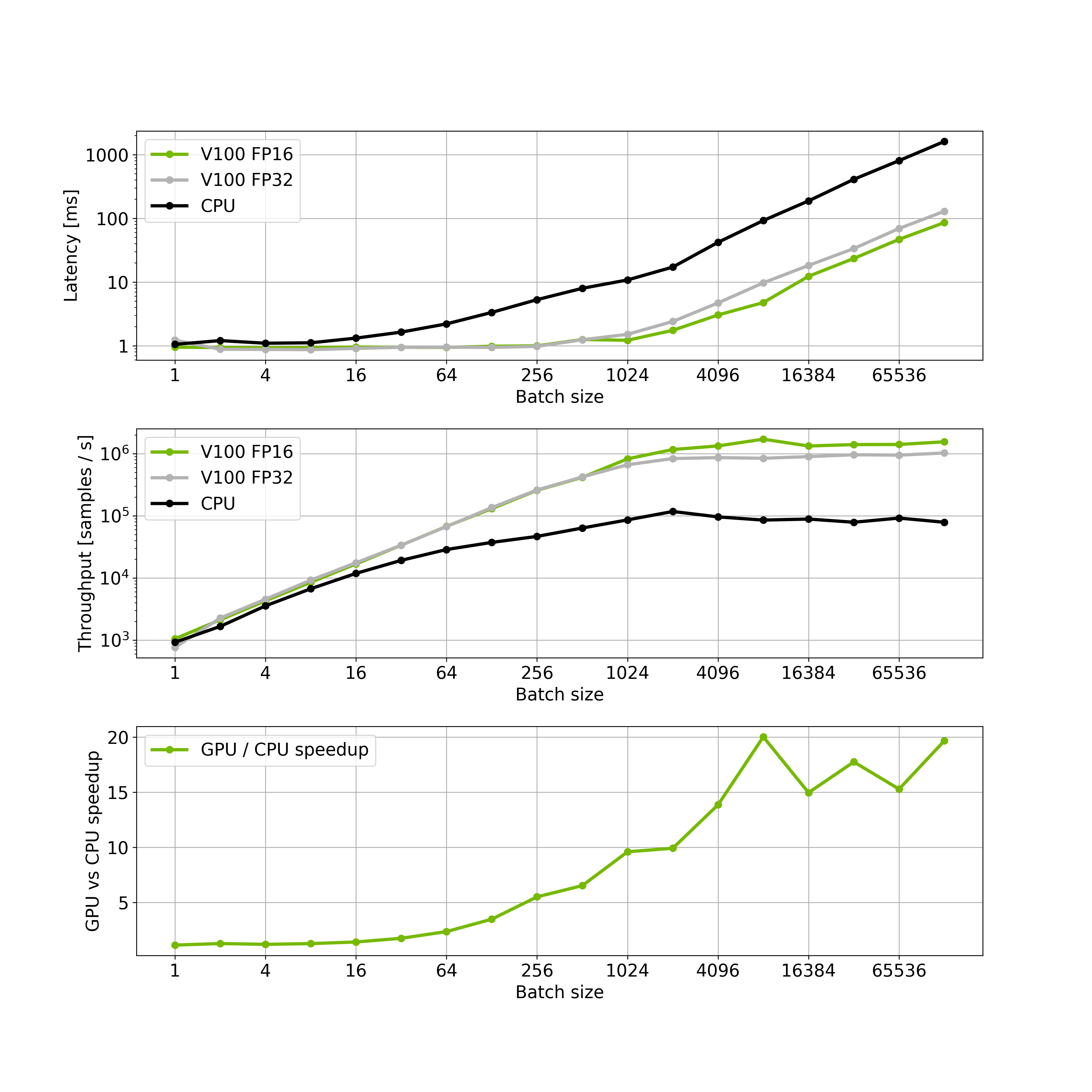
Throughput is measured in recommendations/second, and latency in milliseconds.
TorchScript FP16 inference (V100-32G)
| Batch Size | Throughput [samples / s] | Median Latency [ms] | 95% latency [ms] | 99% latency [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1019 | 0.966 | 1.027 | 1.082 |
| 2 | 2119 | 0.989 | 1.047 | 1.086 |
| 4 | 3340 | 1.199 | 1.277 | 1.290 |
| 8 | 6641 | 1.197 | 1.284 | 1.314 |
| 16 | 12.5k | 1.082 | 1.196 | 1.214 |
| 32 | 28k | 1.133 | 1.271 | 1.291 |
| 64 | 45k | 1.413 | 1.489 | 1.551 |
| 128 | 105k | 1.223 | 1.270 | 1.290 |
| 256 | 193.6k | 1.320 | 1.471 | 1.518 |
| 512 | 376k | 1.367 | 1.449 | 1.486 |
| 1024 | 740k | 1.379 | 1.463 | 1.536 |
| 2048 | 1.105M | 1.817 | 2.106 | 2.195 |
| 4096 | 1.488M | 2.730 | 2.851 | 3.266 |
| 8192 | 1.676M | 4.851 | 5.174 | 5.486 |
| 16384 | 1.831M | 8.926 | 9.127 | 9.415 |
| 32768 | 1.756M | 18.543 | 19.625 | 20.223 |
| 65536 | 1.678M | 38.950 | 41.112 | 41.985 |
| 131072 | 1.547M | 86.258 | 90.772 | 92.511 |
TorchScript FP32 inference (V100-32G)
| Batch Size | Throughput [samples / s] | Median Latency [ms] | 95% latency [ms] | 99% latency [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1153 | 0.855 | 0.909 | 0.929 |
| 2 | 2084 | 0.950 | 1.042 | 1.199 |
| 4 | 4105 | 0.955 | 1.033 | 1.177 |
| 8 | 8356 | 0.943 | 1.029 | 1.179 |
| 16 | 16.8k | 0.942 | 1.009 | 1.158 |
| 32 | 28.3k | 1.134 | 1.274 | 1.336 |
| 64 | 54.7k | 1.214 | 1.307 | 1.353 |
| 128 | 118k | 1.036 | 1.255 | 1.303 |
| 256 | 202k | 1.275 | 1.404 | 1.449 |
| 512 | 401k | 1.286 | 1.365 | 1.397 |
| 1024 | 707k | 1.448 | 1.518 | 1.550 |
| 2048 | 833k | 2.450 | 2.547 | 2.610 |
| 4096 | 1.013M | 3.996 | 4.361 | 4.683 |
| 8192 | 1.091M | 7.333 | 7.951 | 8.115 |
| 16384 | 1.180M | 13.8 | 14.462 | 15.053 |
| 32768 | 1.173M | 27.927 | 28.655 | 28.841 |
| 65536 | 1.140M | 57.046 | 58.627 | 58.861 |
| 131072 | 1.074M | 120.982 | 122.193 | 122.337 |
TorchScript FP32 inference CPU (2x E5-2698 v4 @ 2.20GHz)
| Batch Size | Throughput [samples / s] | Avg Latency [ms] | 95% latency [ms] | 99% latency [ms] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 923.2 | 1.051 | 1.195 | 1.225 |
| 2 | 1660.8 | 1.204 | 1.486 | 1.597 |
| 4 | 3553.6 | 1.095 | 1.456 | 1.65 |
| 8 | 6692.8 | 1.112 | 1.56 | 1.787 |
| 16 | 11.8k | 1.317 | 1.545 | 1.698 |
| 32 | 19.2k | 1.636 | 1.851 | 2.261 |
| 64 | 28.6k | 2.203 | 2.403 | 2.615 |
| 128 | 37.3k | 3.333 | 3.968 | 4.143 |
| 256 | 46.5k | 5.286 | 6.538 | 7.102 |
| 512 | 63.5k | 7.962 | 8.256 | 10.052 |
| 1024 | 85.8k | 10.777 | 16.563 | 17.917 |
| 2048 | 117k | 17.169 | 19.441 | 26.955 |
| 4096 | 95.8k | 41.988 | 45.996 | 50.483 |
| 8192 | 85.1k | 92.251 | 131.333 | 133.578 |
| 16384 | 88.5k | 187.677 | 204.676 | 231.393 |
| 32768 | 78.6k | 408.815 | 428.574 | 429.58 |
| 65536 | 91.8k | 804.059 | 810.328 | 810.328 |
| 131072 | 78.6k | 1606.89 | 1635.36 | 1635.36 |
The plot above shows, that the GPU is saturated with batch size 4096. However, running inference with larger batches might be faster, than running several inference requests. Therefore, we choose 65536 as the optimal batch size.
Advanced
Dynamic batching support
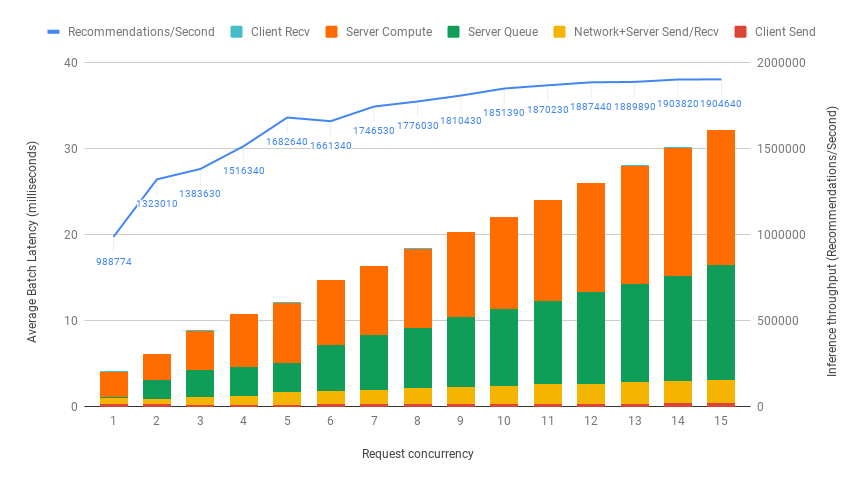
The Triton server has a dynamic batching mechanism built in, that can be enabled. When it is enabled, then the server creates inference batches from the received requests. Since the output of the model is a single probability, the batch size of a single request may be large. Here it is assumed to be 4096. With dynamic batching enabled, the server will concatenate requests of this size into an inference batch. The upper bound of the size of the inference batch is set to 65536. All these parameters are configurable. Performance results on a single V100-32G (ONNX FP16 model) for various numbers of simultaneous requests are shown in the figure below.
The plot above shows, that if we have a 20ms upper bound on latency, then a single GPU can handle up to 8 concurrent requests. This leads to total throughput of 1.776.030 recommendations/sec. This means 35520 recommendations within 20ms, on a single GPU.