11 KiB
Deploying the BERT TensorFlow model using Triton Inference Server
This folder contains instructions for deployment and exemplary client application to run inference on
Triton Inference Server as well as detailed performance analysis.
Table Of Contents
Solution overview
The NVIDIA Triton Inference Server provides a datacenter and cloud inferencing solution optimized for NVIDIA GPUs. The server provides an inference service via an HTTP/REST or gRPC endpoint, or by a C API endpoint, allowing remote clients to request inferencing for any number of GPU or CPU models being managed by the server.
A typical Triton Inference Server pipeline can be broken down into the following steps:
-
The client serializes the inference request into a message and sends it to the server (Client Send).
-
The message travels over the network from the client to the server (Network).
-
The message arrives at the server, and is deserialized (Server Receive).
-
The request is placed in the queue (Server Queue).
-
The request is removed from the queue and computed (Server Compute).
-
The completed request is serialized in a message and sent back to the client (Server Send).
-
The completed message then travels over the network from the server to the client (Network).
-
The completed message is deserialized by the client and processed as a completed inference request (Client Receive).
Generally, for local clients, steps 1-4 and 6-8 will only occupy a small fraction of time, compared to steps 5-6. As backend deep learning systems like BERT are rarely exposed directly to end users, but instead only interfacing with local front-end servers, for the sake of BERT, we can consider that all clients are local.
In this section, we will go over how to launch both the Triton Inference Server and the client and get the best performance solution that fits your specific application needs.
More information on how to perform inference using NVIDIA Triton Inference Server can be found in triton/README.md.
Setup
The repository contains a folder ./triton/ with a Dockerfile which extends the latest TensorFlow NGC container and encapsulates some dependencies. Ensure you have the following components:
-
NVIDIA CUDA repository for NVIDIA TensorRT 7.1.3
-
NVIDIA Volta or Turing based GPU
Quick Start Guide
Running the following scripts will build and launch the container containing all required dependencies for native TensorFlow as well as Triton. This is necessary for running inference and can also be used for data download, processing, and training of the model. For more information on the scripts and arguments, refer to the Advanced section.
- Clone the repository.
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples
cd DeepLearningExamples/TensorFlow/LanguageModeling/BERT
- Build a container that extends NGC TensorFlow, Triton Inference Server, and Triton Inference Client.
bash scripts/docker/build.sh
- Download fine-tuned checkpoints and SQuAD dataset.
To download the data to data/download, run:
bash scripts/docker/launch.sh triton/scripts/triton_data_download.sh
- Run inference.
The Triton Inference Server can serve either of the following two BERT models:
4.1. TensorFlow SavedModel
The run_triton_tf.sh script starts the server on a local host in a detached state, runs the client on the SQuAD v1.1 dataset and then evaluates the validity of predictions on the basis of the exact match and F1 score all in one step.
The script exports the TensorFlow BERT model checkpoint as a tensorflow_savedmodel that Triton Inference Server accepts and builds a matching Triton Inference Server model config when triton_export_model is set to true.
bash triton/scripts/run_triton_tf.sh <init_checkpoint> <batch_size> <precision> <use_xla> <seq_length> <doc_stride> <bert_model> <squad_version> <triton_version_name> <triton_model_name> <triton_export_model> <triton_dyn_batching_delay> <triton_engine_count> <triton_model_overwrite>
Refer to the advanced section for details on launching client and server separately for debugging.
4.2. TensorRT Model
In order to use the BERT TensorRT engine, follow the steps underlined in TensorRT Repository to build a TensorRT engine. Place it as results/triton_models/<triton_model_name>/<triton_version_name>/model.plan and use the run_triton_trt.sh script as follows.
bash triton/scripts/run_triton_trt.sh <batch_size> <seq_length> <doc_stride> <bert_model> <squad_version> <triton_version_name> <triton_model_name>
Notes:
-
Triton Inference Server 20.09 is compatible with TensorRT 7.1.3.
-
The current Triton Inference Server works with the TensorRT engine with
batch_size > 1. -
To use the performance client with dynamic batching, build an engine with -b -b <N+1>` to support dynamic batches upto size N.
Advanced
The following sections provide greater details about the Triton Inference Server pipeline and inference analysis and benchmarking results.
Running the Triton Inference Server
Launch the Triton Inference Server in detached mode to run in background by default. To run in the foreground interactively, for debugging purposes, run:
DETACHED=”-it” bash scripts/docker/launch_server.sh
The script mounts and loads models at $PWD/results/triton_models to the server with all visible GPUs. In order to selectively choose the devices, set NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES.
Running the Triton Inference Client
Real data
In order to run the client with real data, run:
bash triton/scripts/run_client.sh <batch_size> <seq_length> <doc_stride> <triton_version_name> <triton_model_name> <BERT_DIR> <ADDITIONAL_ARGS>
The script calls triton/run_squad_triton_client.py which preprocesses data and sends/receives requests to/from the server.
ADDITIONAL_ARGS must include either --predict_file to use the SQuAD dataset or a sample by passing --question and --context. Append with --trt_engine if running inference on a TensorRT engine server.
Synthetic data
In order to run the client with synthetic data for performance measurements, run:
bash triton/scripts/run_perf_client.sh <model_name> <model_version> <batch_size> <max_latency> <max_client_threads> <max_concurrency> <server_hostname>
The script waits until the server is up and running, sends requests as per the constraints set and writes results to OUTPUT_FILE_CSV="/results/perf_client/${MODEL_NAME}/results_${TIMESTAMP}.csv.
For more information about perf_client, refer to the official documentation.
Performance
The performance measurements in this document were conducted at the time of publication and may not reflect the performance achieved from NVIDIA’s latest software release. For the most up-to-date performance measurements, go to NVIDIA Data Center Deep Learning Product Performance.
Latency vs Throughput for TensorRT Engine
Performance numbers for BERT Large, sequence length=384 are obtained from experiments on NVIDIA A100 with 1x A100 40G GPUs. Throughput is measured in samples/second, and latency in milliseconds.
The plot above shows that throughput gains taper off from increasing batch size above 12. There is minimal gain in throughput going from batch size 12 to 128. However, running inference with a single large batch might be faster than running several small inference requests. Therefore, we choose to maximize batch size for Dynamic Batching with a maximum acceptable queuing delay of 1ms and maximum acceptable inference latency of 100ms.
Dynamic Batching Support
The Triton server has a dynamic batching mechanism built in, that can be enabled. When it is enabled, the server creates
inference batches from the received requests. With dynamic batching enabled, the server will concatenate requests that come in within maximum queue delay time, into a single inference batch. To configure these parameters and run dynamic batching for a model, issue:
#Set server config for dynamic batching with maximum queue delay
echo "dynamic_batching { max_queue_delay_microseconds: 1000 }" >> results/triton_models/bert/config.pbtxt
#Launch Server
DETACHED="-it" bash triton/scripts/launch_server.sh
#Run perf client in another terminal
bash triton/scripts/run_perf_client.sh bert 1 12
Note that the TensorRT engine takes 30+ minutes to build depending on the profile size. Loading it on TRITON server can be sped up by only loading only on required GPUs.
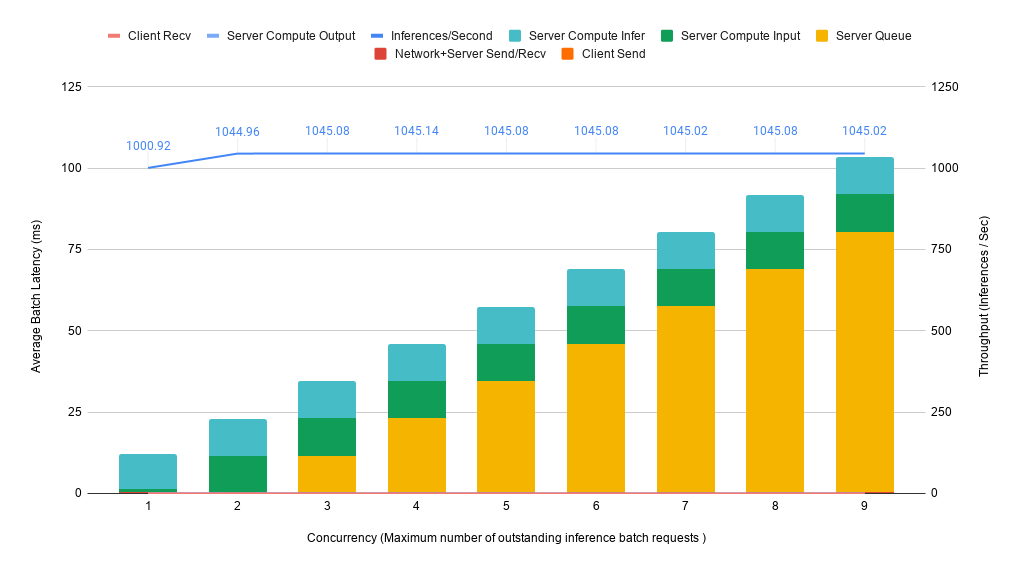
Performance results on a single A100 40G for various numbers of simultaneous requests are shown in the figure below.
The plot above shows that if we have a 100ms upper bound on latency, then a single GPU can handle up to 9 concurrent requests before throughput saturates. This leads to total throughput of ~1045 sequences per second.
Release Notes
Changelog
October 2020 Add scripts to use TensorRT engines for inference
September 2020 Update to TRITON 20.08
April 2020 TRTIS -> TRITON
October 2019 Initial release