33 KiB
Mask-RCNN For TensorFlow 2
This repository provides a script and recipe to train the Mask-RCNN model to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy and is tested and maintained by NVIDIA.
Table Of Contents
- Model overview
- Setup
- Quick Start Guide
- Advanced
- Performance
- Release notes
Model overview
Mask R-CNN is a convolution-based neural network for the task of object instance segmentation. The paper describing the model can be found here. NVIDIA’s Mask R-CNN is an optimized version of Google's TPU implementation, leveraging mixed precision arithmetic using Tensor Cores while maintaining target accuracy.
This model is trained with mixed precision using Tensor Cores on Volta, Turing, and the NVIDIA Ampere GPU architectures. Therefore, researchers can get results 2.2x faster than training without Tensor Cores, while experiencing the benefits of mixed precision training. This model is tested against each NGC monthly container release to ensure consistent accuracy and performance over time.
This repository also contains scripts to interactively launch training, benchmarking and inference routines in a Docker container.
The major differences between the official implementation of the paper and our version of Mask R-CNN are as follows:
- Mixed precision support with TensorFlow AMP
- Gradient accumulation to simulate larger batches
- Custom fused CUDA kernels for faster computations
There are other publicly NVIDIA available implementations of Mask R-CNN:
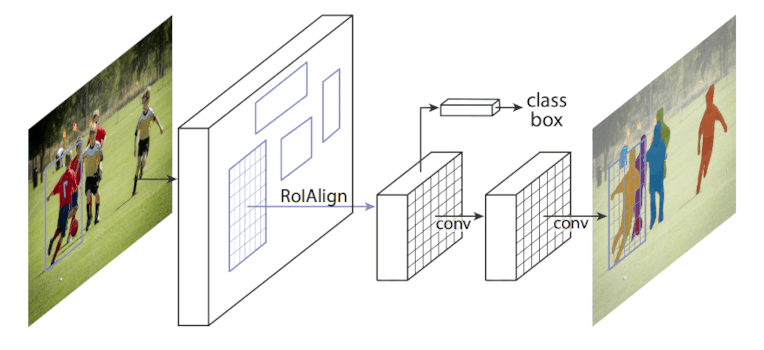
Model architecture
Mask R-CNN builds on top of Faster R-CNN adding a mask head for the task of image segmentation.
The architecture consists of the following:
- ResNet-50 backbone with Feature Pyramid Network (FPN)
- Region proposal network (RPN) head
- RoI Align
- Bounding and classification box head
- Mask head
Figure 1. Diagram of Mask R-CNN framework from original paper
Default configuration
The Mask R-CNN configuration and the hyper-parameters for training and testing purposes are in separate files.
The default configuration of this model can be found at mrcnn_tf2/config.py.
The default configuration is as follows:
- Feature extractor:
- Images resized with aspect ratio maintained and smaller side length between [832,1344]
- Ground Truth mask size 112
- Backbone network weights are frozen after second epoch
- RPN:
- Anchor stride set to 16
- Anchor sizes set to (32, 64, 128, 256, 512)
- Foreground IOU Threshold set to 0.7, Background IOU Threshold set to 0.3
- RPN target fraction of positive proposals set to 0.5
- Train Pre-NMS Top proposals set to 2000 per FPN layer
- Train Post-NMS Top proposals set to 1000
- Test Pre-NMS Top proposals set to 1000 per FPN layer
- Test Post-NMS Top proposals set to 1000
- RPN NMS Threshold set to 0.7
- RoI heads:
- Foreground threshold set to 0.5
- Batch size per image set to 512
- A positive fraction of batch set to 0.25
The default hyper-parameters can be found at mrcnn_tf2/arguments.py.
These hyperparameters can be overridden through the command-line options, in the launch scripts.
Feature support matrix
The following features are supported by this model:
| Feature | Mask R-CNN |
|---|---|
| Automatic mixed precision (AMP) | Yes |
| Accelerated Linear Algebra (XLA) | Yes |
Features
Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP)
This implementation of Mask-RCNN uses AMP to implement mixed precision training. It allows us to use FP16 training with FP32 master weights by modifying just a few lines of code.
XLA support (experimental)
XLA is a domain-specific compiler for linear algebra that can accelerate TensorFlow models with potentially no source code changes. The results are improvements in speed and memory usage: most internal benchmarks run ~1.1-1.5x faster after XLA is enabled.
Mixed precision training
Mixed precision is the combined use of different numerical precisions in a computational method. Mixed precision training offers significant computational speedup by performing operations in half-precision format while storing minimal information in single-precision to retain as much information as possible in critical parts of the network. Since the introduction of Tensor Cores in Volta, and following with both the Turing and Ampere architectures, significant training speedups are experienced by switching to mixed precision -- up to 3x overall speedup on the most arithmetically intense model architectures. Using mixed precision training previously required two steps:
- Porting the model to use the FP16 data type where appropriate.
- Adding loss scaling to preserve small gradient values.
This can now be achieved using Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) for TensorFlow to enable the full mixed precision methodology in your existing TensorFlow model code. AMP enables mixed precision training on Volta, Turing, and NVIDIA Ampere GPU architectures automatically. The TensorFlow framework code makes all necessary model changes internally.
In TF-AMP, the computational graph is optimized to use as few casts as necessary and maximize the use of FP16, and the loss scaling is automatically applied inside of supported optimizers. AMP can be configured to work with the existing tf.contrib loss scaling manager by disabling the AMP scaling with a single environment variable to perform only the automatic mixed-precision optimization. It accomplishes this by automatically rewriting all computation graphs with the necessary operations to enable mixed precision training and automatic loss scaling.
For information about:
- How to train using mixed precision, see the Mixed Precision Training paper and Training With Mixed Precision documentation.
- Techniques used for mixed precision training, see the Mixed-Precision Training of Deep Neural Networks blog.
- How to access and enable AMP for TensorFlow, see Using TF-AMP from the TensorFlow User Guide.
- APEX tools for mixed precision training, see the NVIDIA Apex: Tools for Easy Mixed-Precision Training in PyTorch.
Enabling mixed precision
Mixed precision is enabled in TensorFlow by using the Automatic Mixed Precision (TF-AMP) extension which casts variables to half-precision upon retrieval, while storing variables in single-precision format. Furthermore, to preserve small gradient magnitudes in backpropagation, a loss scaling step must be included when applying gradients. In TensorFlow, loss scaling can be applied statically by using simple multiplication of loss by a constant value or automatically, by TF-AMP. Automatic mixed precision makes all the adjustments internally in TensorFlow, providing two benefits over manual operations. First, programmers need not modify network model code, reducing development and maintenance effort. Second, using AMP maintains forward and backward compatibility with all the APIs for defining and running TensorFlow models.
To enable mixed precision, you can simply add the values to the environmental variables inside your training script:
-
Enable TF-AMP graph rewrite:
os.environ["TF_ENABLE_AUTO_MIXED_PRECISION_GRAPH_REWRITE"] = "1" -
Enable Automated Mixed Precision:
os.environ['TF_ENABLE_AUTO_MIXED_PRECISION'] = '1'
TF32
TensorFloat-32 (TF32) is the new math mode in NVIDIA A100 GPUs for handling the matrix math also called tensor operations. TF32 running on Tensor Cores in A100 GPUs can provide up to 10x speedups compared to single-precision floating-point math (FP32) on Volta GPUs.
TF32 Tensor Cores can speed up networks using FP32, typically with no loss of accuracy. It is more robust than FP16 for models which require high dynamic range for weights or activations.
For more information, refer to the TensorFloat-32 in the A100 GPU Accelerates AI Training, HPC up to 20x blog post.
TF32 is supported in the NVIDIA Ampere GPU architecture and is enabled by default.
Setup
The following section lists the requirements that you need to meet in order to start training the Mask R-CNN model.
Requirements
This repository contains Dockerfile which extends the TensorFlow 2 NGC container and encapsulates some dependencies. Aside from these dependencies, ensure you have the following components:
- NVIDIA Docker
- TensorFlow 21.02 NGC container
- Supported GPUs:
- NVIDIA Volta architecture
- NVIDIA Turing architecture
- NVIDIA Ampere architecture
For more information about how to get started with NGC containers, see the following sections from the NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation and the Deep Learning Documentation:
- Getting Started Using NVIDIA GPU Cloud
- Accessing And Pulling From The NGC Container Registry
- Running [framework name - link to topic]
For those unable to use the TensorFlow 2 NGC container, to set up the required environment or create your own container, see the versioned NVIDIA Container Support Matrix.
Quick Start Guide
To train your model using mixed or TF32 precision with Tensor Cores or using FP32, perform the following steps using the default parameters of the Mask R-CNN model on the COCO 2017 dataset. For the specifics concerning training and inference, see the Advanced section.
-
Clone the repository.
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples.git cd DeepLearningExamples/TensorFlow/Segmentation/MaskRCNN -
Build the Mask R-CNN TensorFlow NGC container.
nvidia-docker build -t nvidia_mrcnn_tf2 . -
Start an interactive session in the NGC container to run training/inference.
Run the following command to launch the Docker container.
docker run --gpus all -it --rm --shm-size=2g --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 nvidia_mrcnn_tf2If you want to reuse the dataset and pretrained ResNet-50 weights between runs, (recommended), use
-v [data directory]:/data -v [weights directory]:/weightsto mount your directories inside the container:docker run --gpus all -it --rm --shm-size=2g --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 -v [data directory]:/data -v [weights directory]:/weights nvidia_mrcnn_tf2The contents of
/dataand/weightswill be downloaded in the following steps. -
Download and preprocess the dataset.
This repository provides scripts to download and extract the COCO 2017 dataset.
If you already have the data, then you do not need to run the following script; instead proceed to the next step. Data will be downloaded to the[data directory]directory provided in step 3.cd dataset bash download_and_preprocess_coco.sh /data -
Download the pre-trained ResNet-50 weights.
This repository also provides scripts to download the pre-trained weights of ResNet-50 backbone. The following script will download the pre-trained weights to
/weights.python scripts/download_weights.py --save_dir=/weights -
Start training.
To run training with a default configuration (on 1/8 GPUs, AMP/FP32), run a
scripts/train.pyscript:python scripts/train.py --gpus {1,8} [--amp]The above script trains a model and evaluates the COCO 2017 dataset using the content in the
/dataand/weightsdirectories. Refer to the Advanced section or runpython scripts/train.py --helpfor more details.
Advanced
The following sections provide greater details of the dataset, running training and inference, and the training results.
Scripts and sample code
Descriptions of the key scripts and folders are provided below.
mrcnn_tf2- Contains source code of this model.main.py- This is the entry point that provides advanced configuration of training and evaluation processes.scripts/- A folder with utility scripts that simplifies running of this model.train.py- Runs training followed by evaluation.evaluate.py- Runs evaluation.inference.py- Runs inference.benchmark_training.py- Script for running train performance benchmarks.benchmark_inference.py- Script for running inference performance benchmarks.download_weights.sh- Can be used to download pre-trained weights for backbone models.
dataset/- A folder that contains shell scripts and Python files to download the dataset.
Parameters
Below you will find a description of the most important parameters accepted by scripts. See Command-line options for list of all available options.
Utility script parameters
All the scripts in the scripts/ directory accept the following parameters:
--batch_size N- Size of the training or evaluation batch size (depends on the script).--amp- When provided, enables automatic mixed precision.--no_xla- When provided, disables XLA (accelerated linear algebra).--data_dir [path]- Path to the directory that contains TFRecords of COCO 2017. Defaults to/data.--model_dir [path]- Output directory for information related to the model that includes model checkpoints. Defaults to/tmp/model.--weights_dir [path]- Directory containing pre-trained ResNet50 weights. Defaults to/weights.
Additionally, training scripts also accept some specific parameters:
train.py--gpus N- Number of GPUs to use during training.--no_eval- When provided, disables evaluation after training.
benchmark_training.py--gpus N- Number of GPUs to use during training.
Note: Any additional flags not specified above will be passed to python main.py. Refer to python main.py --help for a full list of available fags.
Main script parameters
For most use cases, the scripts in scripts/ should be sufficient, but if you need more control over the model, you can also directly execute main.py.
To get the list of all parameters accepted by main.py, run python main.py --help.
Command-line options
To see the full list of available options and their descriptions, use the -h or --help command-line option, for example:
python main.py --help
The following example output is printed when running the model:
usage: main.py MODE [arguments...]
NVIDIA implementation of MastRCNN for TensorFlow 2.x
Runtime:
MODE One of supported execution modes:
train - run in training mode
eval - run evaluation on eval data split
infer - run inference on eval data split
--data_dir DIR Input directory containing the dataset (default: /data)
--model_dir DIR Output directory for information related to the model (default: /results)
--backbone_checkpoint FILE Pretrained checkpoint for resnet (default: /weights/rn50_tf_amp_ckpt_v20.06.0/nvidia_rn50_tf_amp)
--eval_file FILE Path to the validation json file (default: /data/annotations/instances_val2017.json)
--epochs EPOCHS Number of training epochs (default: 12)
--steps_per_epoch STEPS_PER_EPOCH Number of steps (batches) per epoch. Defaults to dataset size divided by batch size. (default: None)
--eval_samples N Number of evaluation samples (default: None)
Hyperparameters:
--train_batch_size N Batch size (per GPU) used during training (default: 4)
--eval_batch_size N Batch size used during evaluation (default: 8)
--seed SEED Set a constant seed for reproducibility (default: None)
--l2_weight_decay L2D Weight of l2 regularization (default: 0.0001)
--init_learning_rate LR Initial learning rate (default: 0.0)
--learning_rate_values [D [D ...]] Learning rate decay levels that are then scaled by global batch size (default: [0.01, 0.001, 0.0001])
--learning_rate_boundaries [N [N ...]] Steps (in epochs) at which learning rate changes (default: [0.3, 8.0, 10.0])
--momentum MOMENTUM Optimizer momentum (default: 0.9)
--finetune_bn Is batchnorm finetuned training mode (default: False)
--use_synthetic_data Use synthetic input data, meant for testing only (default: False)
--xla Enable XLA JIT Compiler (default: False)
--amp Enable automatic mixed precision (default: False)
Logging:
--log_file FILE Output file for DLLogger logs (default: mrcnn-dlll.json)
--log_every N Log performance every N steps (default: 100)
--log_warmup_steps N Number of steps that will be ignored when collecting perf stats (default: 100)
--log_graph Print details about TF graph (default: False)
--log_tensorboard PATH When provided saves tensorboard logs to given dir (default: None)
Utility:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose Displays debugging logs (default: False)
--eagerly Runs model in eager mode. Use for debugging only as it reduces performance. (default: False)
Getting the data
The Mask R-CNN model was trained on the COCO 2017 dataset. This dataset comes with a training and validation set.
This repository contains the ./dataset/download_and_preprocess_coco.sh script which automatically downloads and preprocesses the training and validation sets, saving them to tfrecord files.
Dataset guidelines
The tfrecord files are fed to the model through tf.data.TFRecordDataset() to achieve high performance.
First, the images are normalized using predefined, channel-wise values (offset 0.485, 0.456, 0.406, scale 0.229, 0.224, 0.225). Then, they are augmented (random vertical flip) and resized/padded. The resizing maintains the original aspect ratio while setting the smaller side length to be between 832 and 1344.
The bounding boxes and masks are processed accordingly so that they match the processed images.
Multi-dataset
This implementation is tuned for the COCO 2017 dataset. Using other datasets is possible, but may require changes to the code (data loader) and tuning some hyperparameters (for example, learning rate, number of iterations).
In the current implementation, the data loader works with TFRecord files. If you would like to change the format of the input data, you should substitute the Dataset class which you can find in mrcnn_tf2/dataset/dataset.py.
Training process
Training is performed using the scripts/train.py script which runs main.py with the appropriate flags.
The results are displayed in the console and are saved in ./mrcnn-dll.json (can be overridden by --log_file) in a form of DLLogger logs in which you can find:
- Full configuration used during training
- Losses, learning rate and performance metrics for steps
- Final losses
- Average performance metrics
Additionally, checkpoints will be saved to /tmp/model (can be overridden by --model_dir).
Inference process
Inference is performed using the scripts/evaluate.py script which runs main.py with the appropriate flags.
The results are displayed in the console and are saved in ./mrcnn-dll.json (can be overridden by --log_file) in a form of DLLogger logs in which you can find:
- Full configuration used during the evaluation
- Evaluation metrics
- Average performance metrics
Performance
The performance measurements in this document were conducted at the time of publication and may not reflect the performance achieved from NVIDIA’s latest software release. For the most up-to-date performance measurements, go to NVIDIA Data Center Deep Learning Product Performance.
Benchmarking
The following section shows how to run benchmarks measuring the model performance in training and inference modes.
Training performance benchmark
To run training benchmarking on a selected number of GPUs with either AMP or TF32/FP32 precision, run the following script:
python scripts/benchmark_training.py --gpus {1,8} --batch_size {2,4} [--amp]
Inference performance benchmark
To run inference benchmarking on a single GPU with either AMP or TF32/FP32 precision, run the following script:
python scripts/benchmark_inference.py --batch_size {2,4,8} [--amp]
Results
The following sections provide details on how we achieved our performance and accuracy in training and inference.
Training accuracy results
Training accuracy: NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/train.py --gpus 8 --batch_size 4 [--amp] training script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB) GPUs.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Precision | Final AP BBox | Final AP Segm | Time to train [h] | Time to train speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 2 | TF32 | 0.3796 | 0.3444 | 4.81 | - |
| 8 | 2 | AMP | 0.3795 | 0.3443 | 3.77 | 1.27 |
Training accuracy: NVIDIA DGX-1 (8x V100 16GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/train.py --gpus 8 --batch_size 2 [--amp] training script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with (8x V100 16GB) GPUs.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Precision | Final AP BBox | Final AP Segm | Time to train [h] | Time to train speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 2 | FP32 | 0.3793 | 0.3442 | 11.37 | - |
| 8 | 2 | AMP | 0.3792 | 0.3444 | 9.01 | 1.26 |
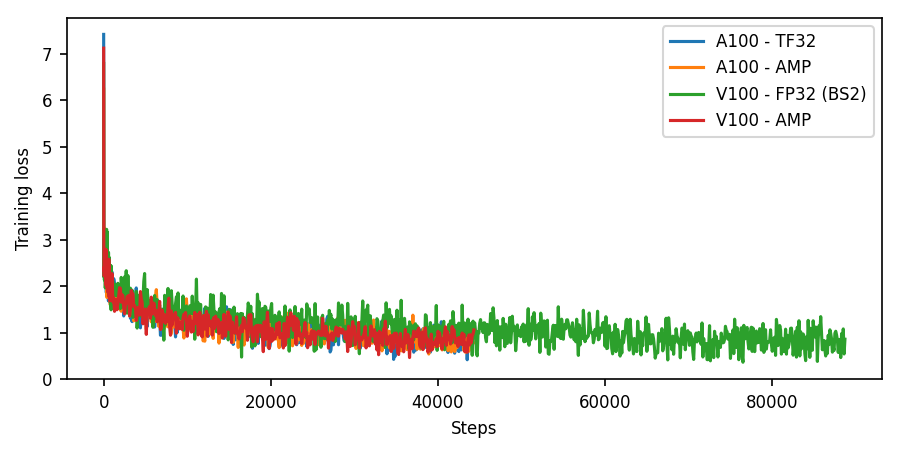
Learning curves
The following image shows the training loss as a function of iteration for training using DGX A100 (TF32 and TF-AMP) and DGX-1 V100 (FP32 and TF-AMP).
Training performance results
Training performance: NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/benchmark_training.py --gpus {1,8} --batch_size {4,8,16} [--amp] training script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (8x A100 80GB) GPUs. Performance numbers (in images per second) were averaged over 200 steps omitting the first 100 warm-up steps.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Throughput - TF32 [img/s] | Throughput - mixed precision [img/s] | Throughput speedup (TF32 - mixed precision) | Weak scaling - TF32 | Weak scaling - mixed precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 13.44 | 18.26 | 1.35 | - | - |
| 1 | 4 | 18.41 | 28.58 | 1.55 | - | - |
| 8 | 2 | 84.29 | 87.31 | 1.03 | 6.27 | 4.78 |
| 8 | 4 | 103.80 | 114.45 | 1.10 | 5.63 | 4.04 |
To achieve these same results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Training performance: NVIDIA DGX-1 (8x V100 16GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/benchmark_training.py --gpus {1,8} --batch_size {2,4} [--amp] training script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with (8x V100 16GB) GPUs. Performance numbers (in images per second) were averaged over 200 steps omitting the first 100 warm-up steps.
| GPUs | Batch size / GPU | Throughput - FP32 [img/s] | Throughput - mixed precision [img/s] | Throughput speedup (FP32 - mixed precision) | Weak scaling - FP32 | Weak scaling - mixed precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 7.57 | 14.47 | 1.91 | - | - |
| 1 | 4 | 8.51 | 19.35 | 2.27 | - | - |
| 8 | 2 | 44.55 | 53.40 | 1.37 | 5.26 | 3.69 |
| 8 | 4 | 50.56 | 58.33 | 1.15 | 6.67 | 4.03 |
To achieve these same results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Inference performance results
Inference performance: NVIDIA DGX A100 (1x A100 80GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/benchmark_inference.py --batch_size {8,16,24} [--amp] benchmarking script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX A100 (1x A100 80GB) GPU.
TF32
| Batch size | Throughput Avg [img/s] | Latency Avg | Latency 90% | Latency 95% | Latency 99% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 39.23 | 0.1530 | 0.1540 | 0.1542 | 0.1546 |
| 12 | 42.55 | 0.2654 | 0.2840 | 0.2875 | 0.2945 |
| 24 | 47.92 | 0.5007 | 0.5248 | 0.5294 | 0.5384 |
FP16
| Batch size | Throughput Avg [img/s] | Latency Avg | Latency 90% | Latency 95% | Latency 99% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 60.79 | 0.0987 | 0.0988 | 0.1000 | 0.1005 |
| 12 | 76.23 | 0.1574 | 0.1614 | 0.1621 | 0.1636 |
| 24 | 80.67 | 0.2975 | 0.3025 | 0.3035 | 0.3054 |
To achieve these same results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Inference performance: NVIDIA DGX-1 (1x V100 16GB)
Our results were obtained by running the python scripts/benchmark_inference.py --batch_size {6,12,24} [--amp] benchmarking script in the TensorFlow 2.x 21.02-py3 NGC container on NVIDIA DGX-1 with (1x V100 16GB) GPU.
FP32
| Batch size | Throughput Avg [img/s] | Latency Avg | Latency 90% | Latency 95% | Latency 99% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 18.56 | 0.3234 | 0.3263 | 0.3269 | 0.3280 |
| 12 | 20.50 | 0.5854 | 0.5920 | 0.5933 | 0.5958 |
| 24 | OOM | - | - | - | - |
FP16
| Batch size | Throughput Avg [img/s] | Latency Avg | Latency 90% | Latency 95% | Latency 99% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 35.46 | 0.1692 | 0.1705 | 0.1707 | 0.1712 |
| 12 | 41.44 | 0.2896 | 0.2937 | 0.2945 | 0.2960 |
| 24 | 42.53 | 0.5643 | 0.5718 | 0.5733 | 0.5761 |
To achieve these same results, follow the steps in the Quick Start Guide.
Release notes
Changelog
February 2021
- Updated implementation to Tensorflow 2, using Keras API and Distributed strategy
- ResNet50 checkpoint now is being downloaded from NVIDIA NGC
- Training using batch size of 8 and 16 can result in unexpected hangs in DGX A100 80GB.
August 2020
- Separated implementation for TensorFlow
1.1xand2.x. New implementation is TF1.1xversion. - Recreated runtime part of the implementation.
June 2020
- Updated accuracy tables with A100 results
- Updated training and inference performance tables with A100 results
November 2019
- Initial release
Known issues
- Out of memory errors can occur when running training, V100, 8GPUs, BS4, FP32.
- Errors can occur when running training with BS1.
- The behavior of the model can be unstable when running with TensorFlow XLA enabled.